Exploring Canadian Watercraft: Tips and Trends
Discover the latest in Canadian watercraft – from Lake Ontario fishing boats to kayaking in the Rockies.
Diving into Marketplace Liquidity Models: Where Buyers and Sellers Dance
Explore the vibrant world of marketplace liquidity models and uncover how buyers and sellers expertly navigate their dynamic dance!
Understanding the Dynamics of Marketplace Liquidity: Key Models Explained
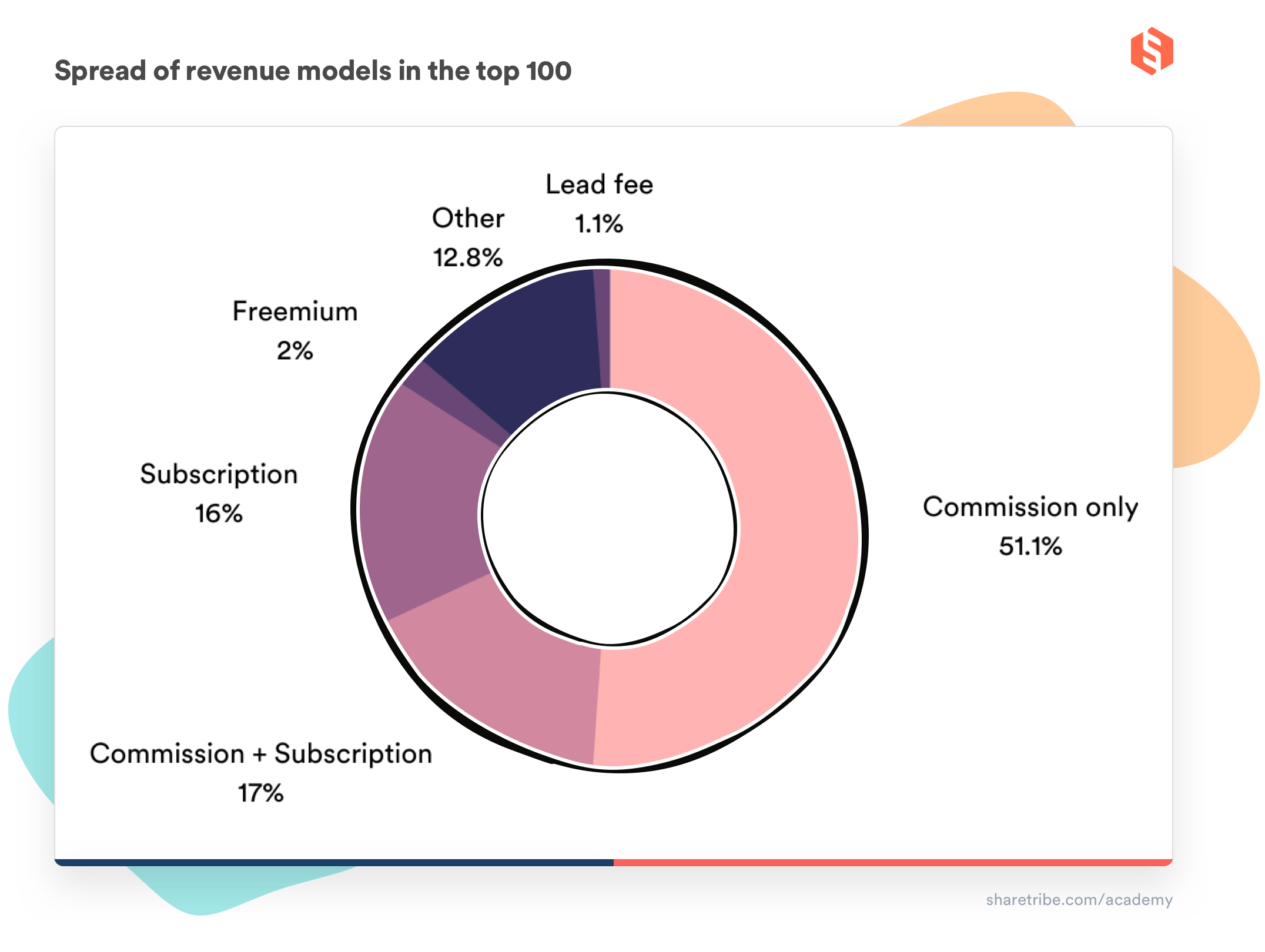
Marketplace liquidity refers to the ease with which assets can be bought or sold in a marketplace without causing significant price fluctuations. Understanding the dynamics of marketplace liquidity is crucial for traders and investors, as it directly impacts their ability to enter or exit positions efficiently. Key factors influencing liquidity include trading volume, market depth, and the presence of market makers. Key models used to analyze liquidity include the Order Book Model, which illustrates the real-time supply and demand for assets, and the Market Impact Model, which assesses how large trades affect prices. By grasping these concepts, participants can navigate marketplaces more effectively and make informed trading decisions.
Another essential aspect of understanding marketplace liquidity is recognizing the different types of liquidity available. For instance, immediacy refers to how quickly a trade can be executed, while cost reflects the price difference between buying and selling an asset. The Liquidity Pool Model illustrates how liquidity is aggregated and provides an overview of the assets available for trading. Additionally, liquidity risk must be considered, as sudden market movements can lead to heightened volatility and potential losses. Familiarity with these liquidity dynamics enables traders to identify optimal entry and exit points, ultimately enhancing their trading strategies.
Counter-Strike is a popular first-person shooter game that emphasizes teamwork and strategy. Players can engage in various game modes, including bomb defusal and hostage rescue. To enhance their gaming experience, many players look for deals and discounts, such as a daddyskins promo code to acquire in-game skins and items.
The Dance of Supply and Demand: How Liquidity Models Impact Your Marketplace
The relationship between supply and demand is fundamental to understanding any marketplace, serving as the backbone for price determination and resource allocation. In this dynamic dance, liquidity models play a crucial role by influencing how quickly assets can be bought or sold without causing significant price shifts. When the market is liquid, participants can readily execute trades, ensuring that supply meets demand efficiently. Conversely, in less liquid markets, small changes in supply or demand can lead to larger price spikes, impacting overall market stability and investor confidence.
Understanding how liquidity models function can provide valuable insights into market behavior. For instance, high liquidity often leads to tighter bid-ask spreads, which can enhance trading volume and attract more participants. In contrast, illiquid markets can deter investment, as traders may fear significant losses due to sudden price changes. Thus, by analyzing these models, businesses and investors can make informed decisions, optimizing their strategies to navigate the complex interplay of supply and demand while maximizing their returns.
What Makes a Marketplace Liquid? Exploring Factors That Attract Buyers and Sellers
Marketplace liquidity refers to the ease with which assets can be bought and sold without causing significant price fluctuations. Several factors contribute to a marketplace's liquidity, including the number of participants, the variety of available assets, and the efficiency of the trading platform. A marketplace that attracts a large number of buyers and sellers generally experiences quicker transactions and less price volatility. Furthermore, a diverse selection of assets not only enhances trading opportunities but also appeals to a broader audience, which can lead to greater liquidity.
Another crucial element that enhances marketplace liquidity is the presence of efficient transaction mechanisms. This includes user-friendly interfaces, real-time data, and effective market-making systems. For instance, platforms that provide instant feedback on market trends and pricing can encourage more active participation. Moreover, liquidity can be significantly influenced by external factors such as regulatory stability, market sentiment, and economic conditions, which play a vital role in attracting new users. In essence, maintaining a liquid marketplace requires a continuous balance of these interrelated factors.